Introduction to Plant-Based Diets and Diabetes Risk
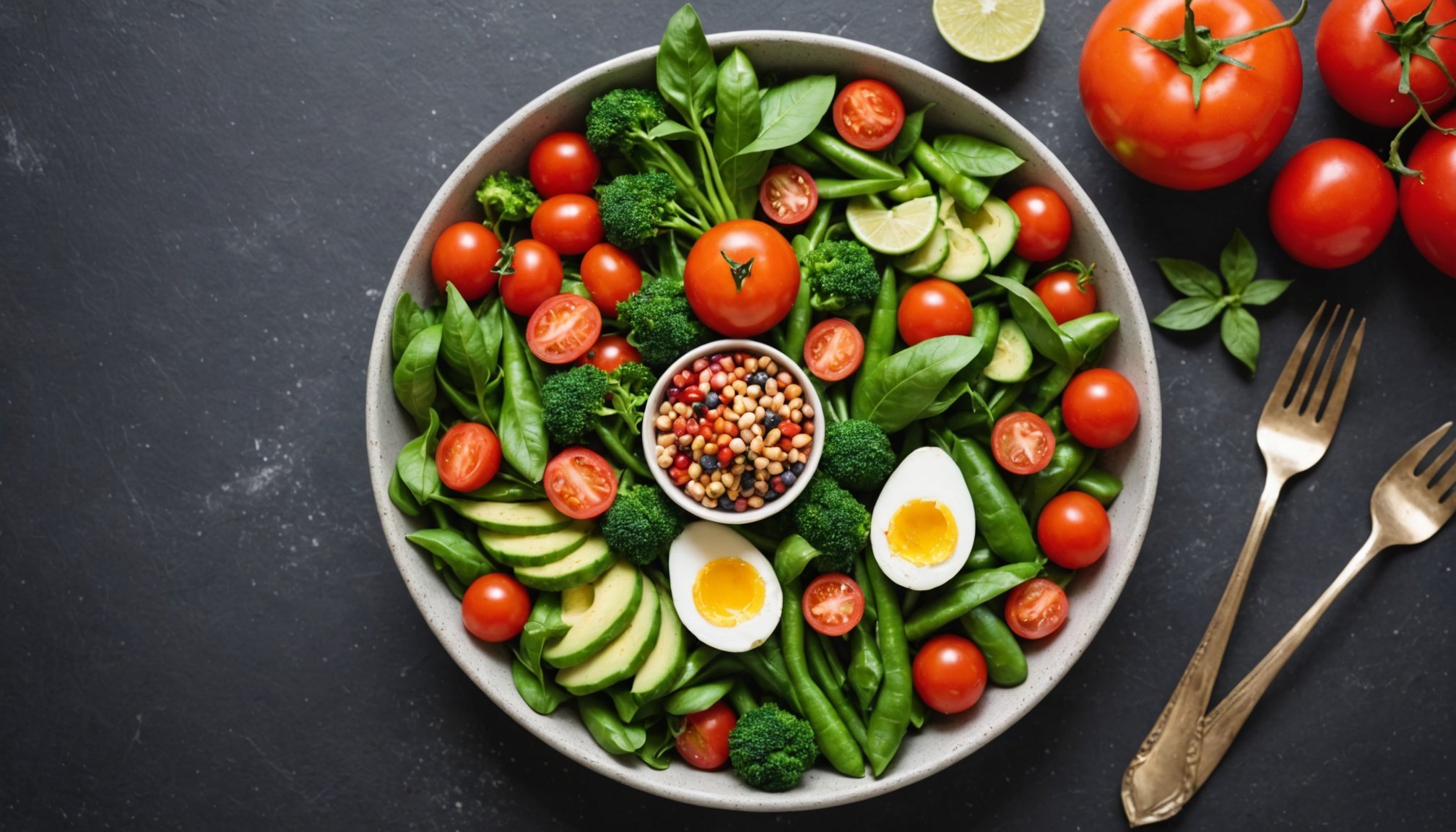
Plant-based diets are increasingly recognised for their role in reducing type 2 diabetes risk. These diets primarily consist of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds while minimising animal products. The core components focus on high fibre, low saturated fats, and beneficial plant compounds. Studies suggest that adhering to a plant-based diet can lead to improved insulin sensitivity and a lower overall diabetes risk.
The statistical link between plant-based diets and reduced type 2 diabetes risk is significant. Research shows that people who follow a plant-rich dietary lifestyle have about a 25% lower risk of developing diabetes compared to those who consume fewer plant-based foods. These findings emphasise the importance of dietary changes in preventive health, especially in the context of chronic diseases like diabetes.
Also to discover : Unlocking the power of social connections: boosting longevity and enriching life for seniors
Understanding and implementing these dietary changes can be a pivotal step toward maintaining health and preventing diabetes. Small, gradual adjustments can lead to more significant lifestyle improvements. As such, embracing a plant-based diet is not just about adopting a particular eating pattern but a proactive approach to long-term health and well-being.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Plant-Based Diets
Eating a plant-based diet has gained traction as an effective strategy for reducing diabetes risk. A broad array of research studies underscores the health benefits of such diets, particularly in diabetes prevention. Let’s explore some of the compelling scientific evidence supporting these claims.
In parallel : Discover the benefits of cold showers: boost your immunity and soothe muscle pain effectively!
Overview of Key Studies
Recent studies have consistently shown that plant-based diets are linked to a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The statistical data is compelling—a notable study revealed that individuals on a plant-rich diet had a 25% reduced risk of diabetes compared to those consuming fewer plant-based foods. Researchers attribute this benefit to the intake of high fibre and low levels of saturated fats present in such diets, which significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
Metabolic Impacts of Plant-Based Eating
The metabolic impact of adopting a plant-based eating pattern is profound. By focusing on foods rich in fibre and beneficial plant compounds, individuals may experience improved metabolic markers. This improvement enhances insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose levels in the blood and lowering diabetes risk. The shift in diet not only aids in weight management but also optimises overall metabolic health, making it a robust approach in diabetes prevention.
Personal Success Stories
Plant-based diets have led to remarkable health transformations for individuals striving to manage or prevent type 2 diabetes. These testimonials provide compelling evidence. Many people share inspiring accounts of their lifestyle changes, where adopting a plant-rich diet reversed diabetes symptoms.
One standout story involves Rachel, who struggled with high blood sugar levels. By shifting to a plant-based diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, she not only managed her sugar levels but also experienced increased energy. Her journey emphasised the significance of dietary lifestyle changes and their impact on health.
Case studies often reveal common themes in successful transformations, such as increased fibre intake and reduced consumption of processed foods. By prioritising whole, unprocessed foods, individuals can effectively support their metabolic health and decrease diabetes risk.
These success stories highlight that while the journey to adopting a plant-based diet may pose challenges, the benefits are substantial. The shared experiences of individuals serve as motivational benchmarks. Embracing a plant-based diet is not merely a dietary adjustment but a commitment to fostering long-term well-being and health.
Practical Tips for Adopting a Plant-Based Diet
Transitioning to a plant-based diet can feel daunting, but with some practical approaches, it becomes manageable and fulfilling. Effective meal planning is a cornerstone, ensuring that daily nutrition needs are met without stress. Start by incorporating plant-based ingredients slowly into your existing meals. For example, replace ground beef with lentils in tacos or hamburgers, offering a tasty and nutritious alternative.
Simple Substitutions for Everyday Meals
Make easy substitutions to familiar dishes. Replace dairy milk with almond or oat milk in cereals and coffees. Try swapping eggs with chia seeds or mashed bananas in baking recipes. All these options support a smoother dietary transition while maintaining meal enjoyment.
Creating Balanced Plant-Based Meals
Building nutritionally balanced meals is crucial. Ensure you’re getting a mix of proteins, healthy fats, and carbohydrates. Pair beans with grains, such as rice or quinoa, to complete your protein intake and include plenty of vegetables for essential nutrients.
Shopping Strategies for a Plant-Based Lifestyle
Developing a strategic shopping list can simplify this lifestyle shift. Focus on whole and minimally processed foods, like fresh produce, nuts, and whole grains. Stick to the outer aisles of the grocery store, where these wholesome ingredients are typically found.
Addressing Misconceptions About Plant-Based Diets
Despite the growing popularity of plant-based diets, several myths and misconceptions persist. A common myth is that plant-based diets lack adequate protein sources. In reality, many plants, such as lentils, beans, and quinoa, provide substantial protein, fulfilling dietary needs effectively. Additionally, plant-based diets are often criticised for being nutritionally insufficient. However, with proper planning, they can supply all essential nutrients.
Clarifying these misconceptions is crucial for individuals considering dietary changes. Vitamin B12, often mentioned in discussions, is indeed limited in plant foods but can be obtained from fortified products or supplements. Nutrition education plays a pivotal role in debunking these myths and guiding individuals toward a well-rounded plant-based diet.
Educational resources, such as cooking classes or workshops, offer valuable insights into meal planning, helping individuals meet their nutritional requirements confidently. Online forums and communities can also provide support and knowledge sharing, dispelling myths through collective experiences.
Understanding the reality of plant-based nutrition is essential for anyone looking to decrease their risk of diabetes while enjoying a diverse and nutrient-rich diet.
Challenges of Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
Transitioning to a plant-based diet often presents certain obstacles for individuals. Changes in dietary habits can be challenging due to ingrained cultural food practices, availability of plant-based options, or lack of culinary skills. Understanding these barriers can help in addressing them effectively.
Common Challenges Faced
Many individuals find it difficult to give up the comfort and familiarity of habitual meals. Limited availability of plant-based alternatives in certain regions may also hinder the transition. Emotional and social factors, such as family preferences or cultural expectations, can further complicate the adoption of new eating patterns.
Strategies to Overcome Dietary Hurdles
To navigate these challenges, consider gradual dietary changes. Start by incorporating more fruits and vegetables into existing favourite dishes. Experiment with diverse flavours and spices to simulate your accustomed tastes. Access online platforms and local communities for support systems and practical meal ideas, ensuring you remain motivated.
Building a Support Network
A strong support network can significantly ease the transition. Engage with friends, family, or online groups who share the same dietary interests. Participating in cooking workshops or joining supportive communities can provide encouragement and useful tips, making the journey more enjoyable and sustainable.
Conclusion and Encouragement to Transform Health
Embracing lifestyle changes by adopting a plant-based diet can significantly transform one’s health journey. From reducing type 2 diabetes risk to enhancing overall metabolic health, plant-based eating presents a myriad of benefits. By making intentional dietary changes, individuals can embark on a proactive health path that prioritises long-term vitality.
Considering dietary adjustments might initially seem overwhelming. However, the rewards, such as risk reduction for diabetes and improved well-being, are substantial. These dietary shifts call on readers to evaluate their eating habits critically and explore how plant-based foods can complement their lifestyle goals. Taking small, manageable steps, like incorporating more fruits and vegetables into meals, can lead to significant health improvements over time.
For those looking to embark on this path, there is encouragement in knowing that the plant-based lifestyle is supported by a robust community and extensive resources. Engaging with others who share similar dietary interests, attending workshops, and utilising online platforms can offer guidance and inspiration. As you consider this dietary transformation, keep in mind that each small step is a stride towards healthier living and a promising future.