H2 – Understanding Overmedication in Seniors
The term overmedication refers to the use of unnecessary or excessive medications, which is alarmingly prevalent among seniors. This group often experiences higher rates of prescriptions, putting them at greater risk for health complications. A significant contributor to this issue is the increase in chronic conditions commonly managed with pharmaceuticals, often leading to unintentional overmedication.
Definition and Prevalence
Overmedication in the elderly is a growing concern, as many seniors fail to recognize its occurrence. Often taking more medications than necessary, about 20-40% of older adults deal with potential redundancy in their pharmaceutical regimens, a serious threat to their health.
In parallel : Key factors to choose the ideal hearing aid for seniors experiencing hearing impairment
Common Health Risks
This phenomenon can lead to severe health risks, including increased cognitive impairments and a heightened susceptibility to adverse drug reactions. Conditions like dizziness or liver damage are just two of many potential outcomes.
Importance of Medication Management
Effective medication management can’t be underestimated. Proper strategies can safeguard seniors against the risks associated with overmedication. By implementing thorough review processes and ensuring clarity and precision in prescriptions, healthcare providers play a crucial role in the well-being of the elderly. Addressing this issue proactively through mindful medication practices ensures enhanced quality of life for seniors.
Also read : Navigating the pros and cons of downsizing homes: a senior”s guide to life after retirement
Essential Indicators of Overmedication
Understanding the signs of overmedication is crucial for timely intervention in seniors. Tracking both physical and behavioural shifts can offer insights into potential medication excess.
Physical Indicators
Physical symptoms of overmedication may include noticeable changes in vital signs such as blood pressure or heart rate. Seniors might also experience unexplained weight fluctuations, either as gain or loss, raising further concerns. Moreover, an increased risk of falls signifies a critical physical indicator, where dizziness or imbalance could stem from excessive medications. These symptoms demand immediate attention to prevent dangerous outcomes.
Behavioral Indicators
Behavioural signs include cognitive issues such as confusion or a sudden decline in mental clarity. If sedation or extreme fatigue is observed, it is another red flag, suggesting the effects of overmedication. Coupled with these symptoms, withdrawal from social interactions can signal a deeper underlying issue, as seniors become less socially engaged due to medication impacts.
Health Issues Linked to Overmedication
Frequent emergency room visits can indicate pervasive complications stemming from too many prescriptions. Likewise, the emergence or aggravation of chronic conditions might suggest medication-related problems. Attention must focus on medication side effects, where symptoms or conditions deteriorate, often pointing to an overwhelmed pharmaceutical regimen.
Strategies for Identifying Overmedication
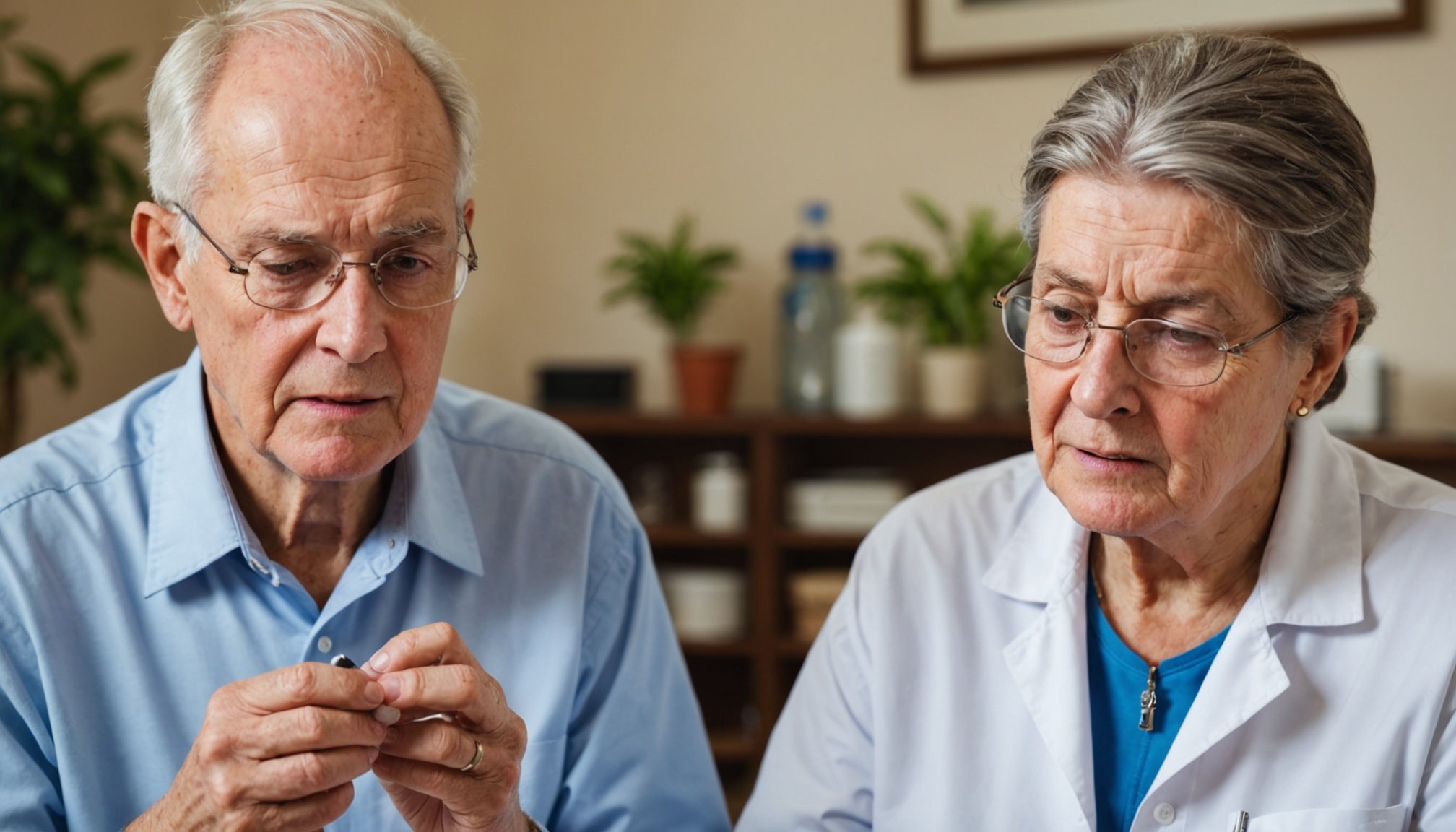
Medication reviews form a pivotal part of identifying and addressing overmedication in seniors. Regular assessments by healthcare professionals can significantly mitigate the risks associated with excessive pharmaceuticals. These reviews involve evaluating all prescribed and over-the-counter medications, ensuring that each is necessary and beneficial for the individual’s current health status.
To effectively monitor medication effects, healthcare professionals should employ techniques that capture changes in the senior’s health both physically and behaviourally. Tracking metrics such as blood pressure, weight, and balance, alongside cognitive assessments, can provide valuable insights into potential medication excess.
Family members play an equally critical role in managing medication schedules. Involving them in the medication review process enhances the identification of symptoms that may go unnoticed by medical personnel. They can offer observations on behavioural shifts, like increased confusion or fatigue, that can signal overmedication issues.
Additionally, educating both seniors and their families about medication side effects promotes informed decision-making. This combined effort ensures a robust support system, helping seniors maintain a healthier balance between necessary treatment and minimizing harm from unnecessary medication use.
Proven Management Techniques
What are the most effective medication management strategies for seniors? Engaging in regular medication reviews and refining communication with healthcare providers play critical roles in minimizing the potential for overmedication. Let’s explore techniques that ensure optimal medication use while safeguarding senior health.
Conducting Medication Reviews
Conduct regular medication reviews to avoid issues like polypharmacy, where patients are prescribed too many medications. Pharmacists can play a crucial role, offering insights into medication interactions and alternatives. Aim to review medications every six months, ensuring each prescription aligns with current health needs while minimizing unnecessary drugs.
Effective Communication with Healthcare Providers
How do you effectively discuss medications with your healthcare team? Initiate discussions by maintaining a comprehensive medication list, noting any side effects. Use this list to collaborate with your providers, forming a cohesive strategy that prioritizes senior safety and effectiveness. Building a supportive care team involves regular updates and open communication.
Educational Resources for Caregivers
Caregivers can significantly benefit from training programs that deepen their understanding of medication impacts. Additionally, online resources and communities empower caregivers with the knowledge to make informed decisions. Personalised medication plans with safety checks help in ensuring the balance between essential treatments and potential overuse.
Case Studies and Practical Examples
Exploring real-life examples provides valuable insight into managing overmedication in seniors. By analysing case studies, we uncover practical strategies deployed by caregivers and healthcare professionals that demonstrate successful management of medication use.
Case Study Analysis
A notable case study involved a senior living with multiple chronic conditions. Through consistent medication reviews and close monitoring by healthcare providers, unnecessary medications were identified and carefully reduced. This proactive approach highlighted the effectiveness of regular reviews in preventing overmedication-related issues, maintaining their health without compromising necessary treatments.
Practical Strategies
In another scenario, a caregiver observed gradual changes in a senior’s behaviour, including increased fatigue and confusion. By engaging with healthcare professionals, these concerning signs were addressed swiftly, leading to a tailored medication plan that significantly enhanced the individual’s quality of life.
Lessons learned from these examples emphasize the importance of vigilance and communication between caregivers and healthcare teams. By fostering collaborative strategies, it is possible to optimize medication regimens, reducing potential harm.
Best Practices
- Continual education for caregivers through programs and resources.
- Establishing a cohesive care team to routinely reassess medications.
- Encouraging open channels of communication with healthcare professionals.
These practices ensure seniors receive appropriate care levels while minimizing overmedication risks.